Mapped: Covid-19 'increasing in every area of UK except these four locations'


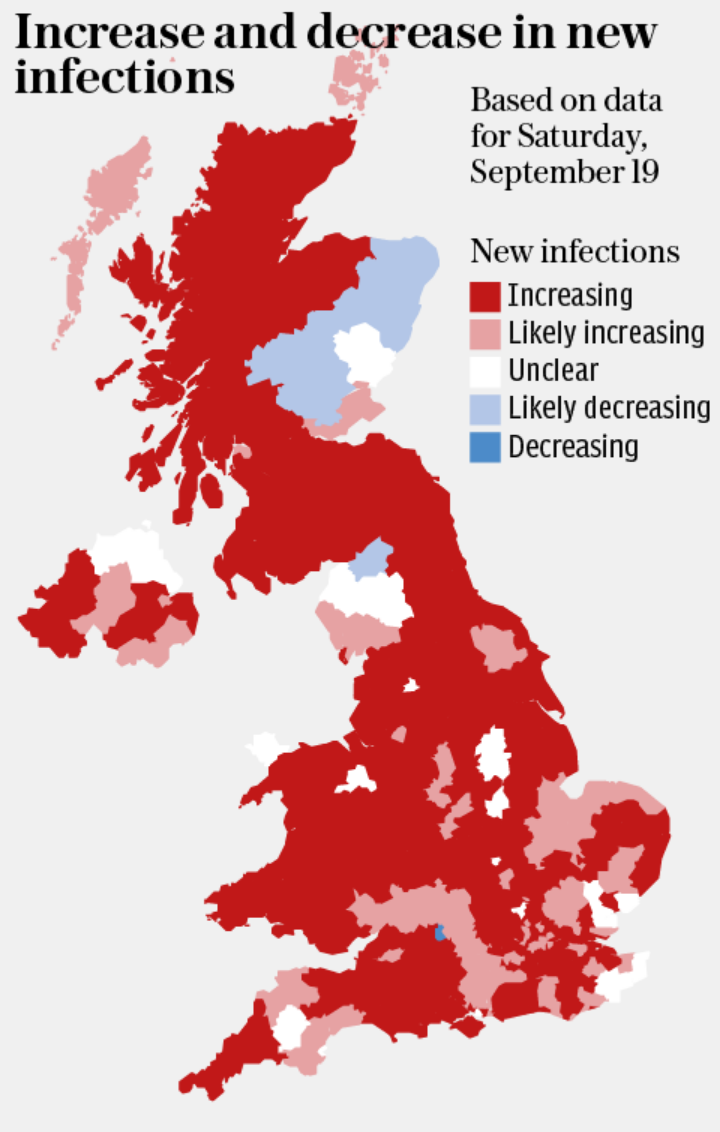
Coronavirus is increasing in every area of the UK except Carlisle, Swindon, Aberdeenshire and Perth and Kinross, Imperial College London modelling suggests.
Researchers from the university’s Department of Mathematics have used infection and deaths data to estimate how the virus is spreading and where the next Covid hotspots are likely to be.
The stark predictions, which show huge swathes of the UK experiencing a rise in cases with more hotspots predicted, came as Professor Neil Ferguson, whose modelling helped shape Britain’s response to the virus, warned new restrictions needed to be imposed “sooner rather than later”.
Meanwhile writing in The Sunday Telegraph, Professor Mark Woolhouse has said it is “profoundly disappointing” the Government keeps returning to lockdowns, despite the strategy “visibly failing around the world”.
The Edinburgh University professor of infectious disease epidemiology wants a strategy which avoids “crippling on/off cycles” of lockdowns, but lets each person assess risks while the vulnerable are protected.
More than 13 million people in the UK – roughly one in five – are enduring local restrictions. The Imperial team has predicted clusters of local authority areas where there is a high probability of hotspots in three weeks.
The modelling (see graphic below) shows a cluster in the Home Counties, with Windsor and Maidenhead, Spelthorne and Hertsmere most at risk. It predicts Redbridge could be London’s first hotspot.
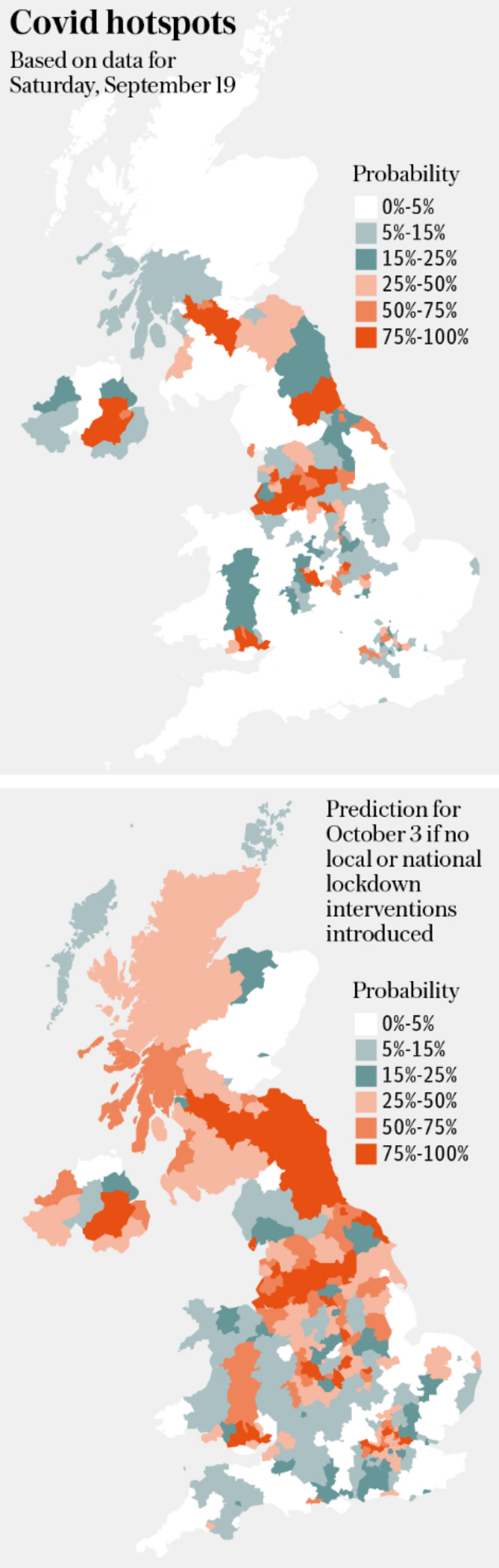
It also suggests the likelihood of transmissions increasing around areas where new restrictions or local lockdowns have already been imposed in the Midlands, South Wales, the North East and parts of Scotland.
The team uses data from daily cases of infections and weekly deaths as well as mathematical modelling to draw up a percentage probability of a region becoming a hotspot.
The map gives estimates of the reproduction or R number. It then predicts how it could develop. The team defines a hotspot as a local authority where there are more than 50 cases of Covid-19 per 100,000 per week.
Professor Axel Gandy, lead researcher, said: “The model allows us to project where local hotspots of Covid-19 are likely to develop based on the trends that we’re seeing.”

The current national R number has increased to between 1.1 to 1.4. A further 4,422 confirmed cases of coronavirus have been recorded in the UK, bringing the overall total to 390,358.
The Government announced on Saturday a further 27 people died within 28 days of testing positive, bringing the total in Britain to 41,759.
Professor Ferguson said the country was facing a “perfect storm” following the easing of restrictions.
“We are at about the levels of infection we were seeing in late February,” he told the Today programme on BBC Radio 4.
“If we leave it another two to four weeks we will be back at levels we were seeing more like mid-March. That’s clearly going to cause deaths because people will be hospitalised. I think some additional measures are likely to be needed sooner rather than later.”
He added: “We have in some sense a perfect storm of getting back to normal, schools reopening, a surge in cases so therefore the testing system is under strain. So unfortunately we do have to roll the relaxation of measures back a little bit and get contacts down.”
He said the Government needs to develop a set of “sustainable” coronavirus restrictions to avoid repeated lockdowns. “My own view is a temporary lockdown – it wouldn’t be like it was in March, it would be less restrictive than that – would pull down infection numbers to allow the testing system to cope a bit better.
‘‘But I think actually what we want is to have a set of sustainable measures through until we have a vaccine, not go through this cycle again.”
Professor Robert Dingwall, a sociologist and part of the New and Emerging Respiratory Virus Threats Advisory Group, said there was a sense the Government was “jumping the gun a little” by considering a new lockdown.
“It’s a little bit premature to say we are on this exponential growth curve when we may just be drifting up to another stable situation at a slightly higher level,” he told Newsnight.
He added that some question “whether the public will stand for this much longer”.

