First China manufacturing shrinkage in 7 months: HSBC
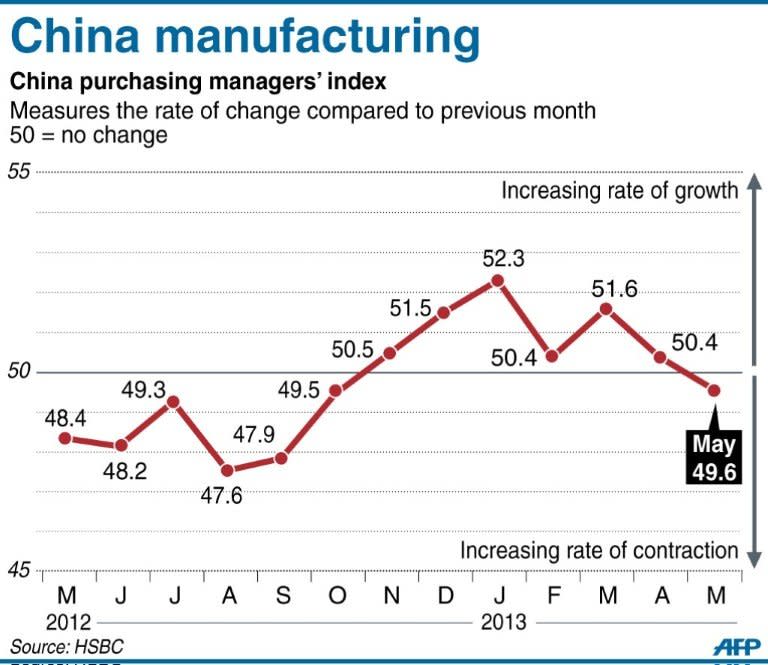
Manufacturing activity in China contracted in May for the first time in seven months, HSBC said Thursday, in another sign of the weakness of recovery in the world's second-largest economy. The British banking giant's preliminary purchasing managers' index (PMI) fell to 49.6 this month from a final 50.4 in April, putting it below the 50 mark that indicates contraction. A reading above signals expansion. It was the lowest figure since October's 49.5, according to the bank's data, and the first time it had been below 50 since then. The index tracks manufacturing activity and is a closely watched barometer of the health of the economy. The final result for May will be released on June 3. Analysts said the figure was the result of both domestic and overseas economic woes. "The cooling manufacturing activities in May reflected slower domestic demand and ongoing external headwinds," said Qu Hongbin, an HSBC economist in Hong Kong, adding the slowdown cast "downside risk to China's fragile growth recovery". The government should provide more support for the sluggish job market, possibly through measures such as training subsidies and tax cuts for employers, he said in a statement. China grew at its slowest pace in 13 years in 2012, with gross domestic product expanding 7.8 percent in the face of weakness at home and in key overseas markets. Economic growth rebounded to 7.9 percent in the final quarter of 2012, raising hopes of recovery, but fell back to 7.7 percent in January-March, with other recent indicators also dampening expectations. Societe Generale economist Yao Wei said the initial PMI figure suggested destocking was continuing and the employment situation had deteriorated, bad signs for consumption going forward. "This reading bashes the hope of a second-quarter growth recovery, meaning that the second quarter GDP growth now looks very likely to be even lower than first quarter," she said. "We just don't see much growth momentum at all for the Chinese economy." Chinese leaders have said expansion will slow in the next stage of the nation's development from the near-double-digit yearly rises of recent decades, as they try to retool the economy to emphasise consumer demand as the key growth driver, rather than investment and exports. The government has set its economic growth target for this year at 7.5 percent. China normally exceeds its stated growth goals, but Yao said actual expansion could fall short of the target given the current economic situation. "Anything above seven percent" might still prove acceptable to China's new leaders, she added. "The key right now for the government is the job market. If the job market continues to hold, there is really not so much they would do about the cyclical growth."